Cut, fall, or bad knock suddenly can cause a wound. Examples of wounds are cuts, lacerations, and grazes. Cuts are generally caused due to sharp objects like knives, blades, broken glass, and metal sheets. Grazes (also called abrasion) is a superficial injury in which the top layer of skin is damaged by friction. Grazes can occur when a person falls off a skateboard or bicycle and the body crosses the ground. “Road rash” is the term used to describe injuries caused by cyclists and motorcyclists rubbing their skin against the road surface. A laceration is a tear in skin tissue caused by shear or crushing forces. Injuries are often because of blunt force trauma. A laceration can also be described as an incomplete separation of strong tissue elements such as blood vessels and nerves.
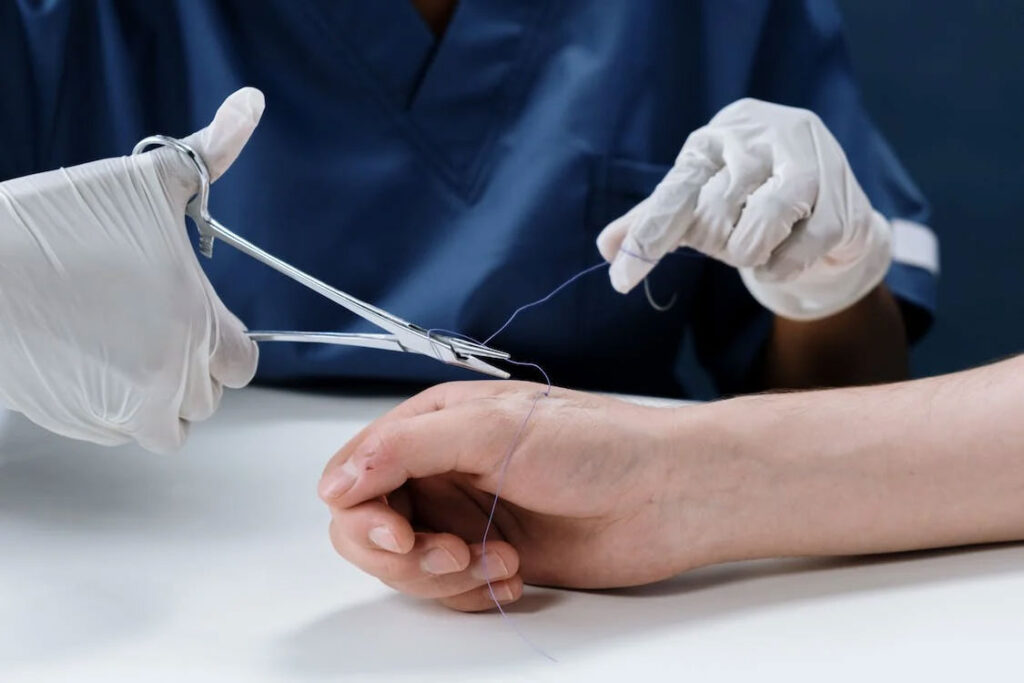
What Are Stitches?
Your skin’s stitches function similarly to the ones in your clothes as a strand of thread to hold things together. They are composed of a variety of materials, including silk and nylon. Some even dissolve on their own, like the ones used for oral injuries.
Stitching is important when needed for the following reasons:
- Gives support and strength when the skin closes the wound.
- Reduces risk of bleeding and infection.
- Minimize scarring.
Call for emergency if the wound is severe, dial 911 if the wound is:
- Bleeding in excess
- Bleeding does not stop after 10 minutes to pressure
- Spurts blood
- Neck, chest, or abdomen is wounded
- Severe pain, fast breathing or trouble breathing, dizziness, unconsciousness, vomiting
- Cut on the face, eyelids, or genitals
- Animal bite
- Loss of sensation
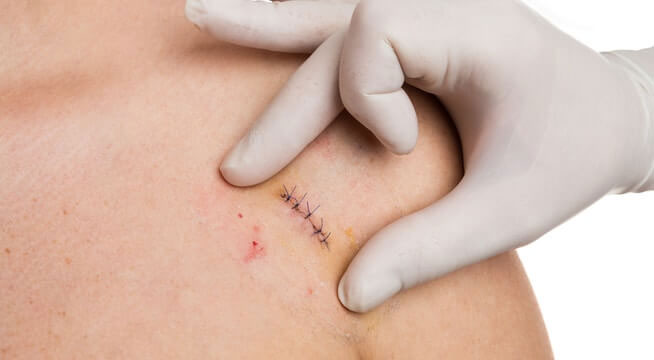
When does the wound need stitches?
A wound may require stitches or other medical procedures if it meets any of the following criteria:
- If the cut is deeper than a quarter inch.
- If the cut is because of a dirty or rusty object and at risk of infection.
- Because of the wound, fat, muscle, bone, or other deep body structures are visible.
- The wounds are deep, on the hands or fingers.
- The wound is over a joint
- After 15 minutes of pressure, the wound is still bleeding.
- You are worried about the wound’s appearance since it is on a face or other region where you don’t want a scar.
A cut may not require medical attention if:
- The edges of the cut are smooth and stay together as you move.
- The wound is very shallow.
- It is a puncture wound (the wound is usually smaller, has less risk of scarring, and is more difficult to clean, so closing the wound increases the risk of containing infection-causing bacteria that may grow inside. increase).
Getting Stitches at Texas Specialty Clinic:
- Wound Care for deep cuts, uncontrollable or severe bleeding, and animal attacks is available at Texas Specialty Clinic.
- Our healthcare professionals are well-trained and experienced in the treatment of wounds and stitching the wound carefully.
- The doctors look after all kinds of wound conditions by giving careful treatment to the patients.
- Texas Specialty Clinic has all the necessary tools for the treatment of wounds
- Call for medical care immediately if you experience severe cuts, an animal attack, or a fall.
- For wound treatment visit Texas Specialty Clinic, book an appointment by dialing (469) 545-9983 .
What to do before reaching the doctor?
- Leave the object as it is: If anything is stuck in your skin, such as a nail, leave it there. The bleeding could be prevented from getting worse. However, if the object that caused the hole is minor and simple to remove, do so.
- Do not eat or drink: This is mainly for children. You may need a calming medicine so that the doctor can stitch up the wound. If you eat or drink anything, they may have to wait longer for treatment.
- Apply pressure: Direct pressure should be applied to the wound using a clean cloth or bandage. Try to hold the injured area above your heart to stop or slow bleeding. Don’t remove the old bandage if blood seeps through it. Simply place a new one on top of the old one.
- Clean the wound: Clean the wound if possible. Do not use peroxide or iodine. Both can irritate wounds. Also, avoid scrubbing. Instead, you can:
- Wash hands properly with soap and water.
- Clean the wound with running tap water. Then, if possible, wash the wounded area with mild soap and water and rinse again.
- Pat the affected place dry with a clean towel. Avoid fluffy clothes that can stick to the wound such as cotton balls.
- Apply antibiotic cream.
- Place a clean bandage over it to protect the wound from dirt and further injury.
If you experience a severe wound, visit the doctor immediately to avoid more damage in the future, contact Texas Specialty Clinics to heal faster, call us at (469) 545-9983, and get treatment from experienced doctors.
