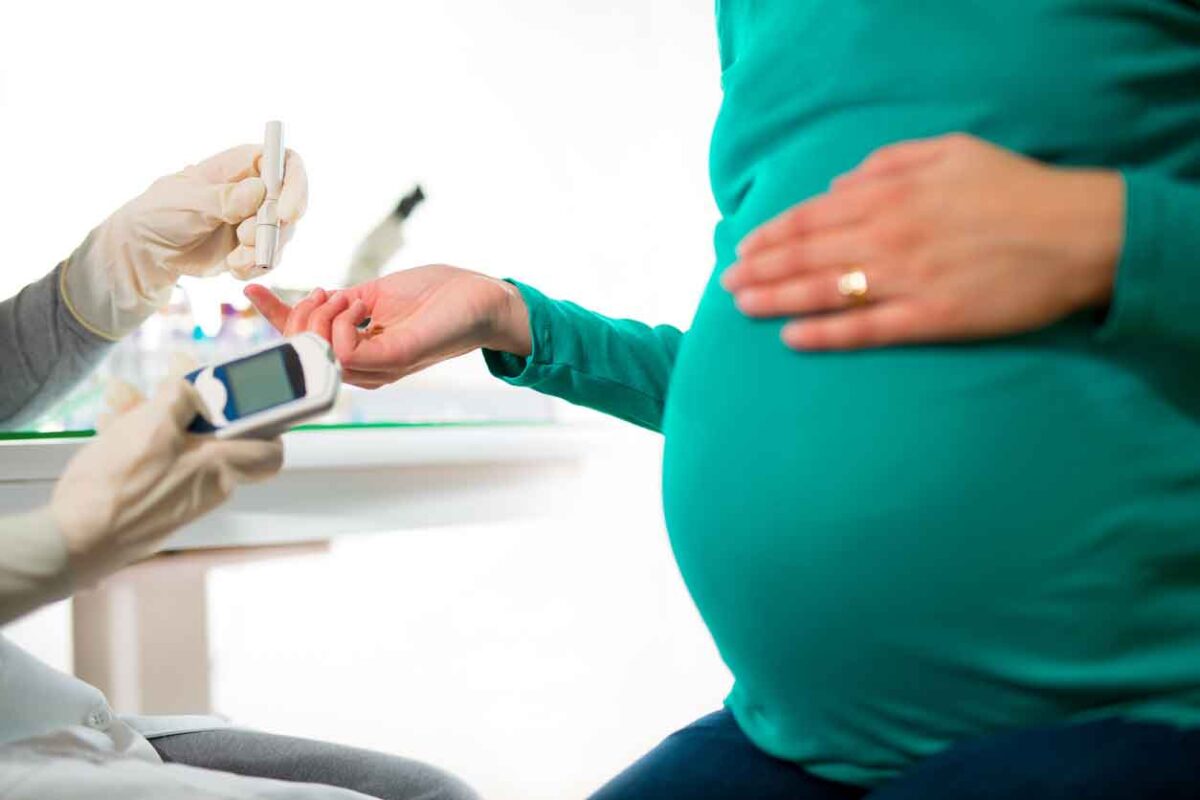
When you are pregnant, your cells become somewhat more resistant to insulin. That raises how much sugar is in your blood, which helps make more nutrients accessible to your baby. Yet, assuming that the degree of glucose turns out to be excessively high, it can bring on some issues for yourself as well as your baby.
Gestational diabetes is a health condition that includes high levels of glucose in the blood while a lady is pregnant. While most ladies with gestational diabetes have ordinary pregnancies and bring forth healthy children, there are various complications that are bound to happen in moms with uncontrolled gestational diabetes.

What Types Of Diabetes Can Occur In Pregnancy?
When a baby is born to a mother with diabetes, the baby is in danger of problems. Individuals with diabetes have high levels of sugar in their blood (hyperglycemia). Over the long run, this can prompt serious health problems. Monitoring your glucose lowers your gamble of complications. You can oversee diabetes by eating a healthy diet, getting standard activity, and taking medication.
Two types of diabetes can affect you during pregnancy. These include :
- Gestational diabetes : You don’t have diabetes before pregnancy in this condition. You develop diabetes during pregnancy and it usually goes away after your baby is born.
- Pregestational diabetes : You have diabetes before getting pregnant in this condition.
If you are diagnosed with type 1 diabetes your body doesn’t produce insulin. Your body needs insulin to utilize glucose. You’ll have to make insulin efforts. People with type 2 diabetes can’t utilize the insulin they make. Or on the other hand, their bodies don’t make enough insulin. You’ll require glucose-lowering medication and conceivably insulin. It’s critical to deal with your glucose during pregnancy. This can bring down your baby’s risk of problems.
How Can Gestational Diabetes Be Harmful To Your Baby?
In pregnancy, the placenta gives the developing baby nutrients and water. It likewise makes the hormones you want for a healthy pregnancy. Few of these hormones can block insulin. This frequently begins at 20 to 24 weeks of pregnancy.
As the placenta develops, it makes more of these hormones. This implies that the pancreas should make more insulin. Ordinarily, the pancreas can make enough insulin. If it doesn’t, gestational diabetes happens. Pregnancy may likewise change the insulin needs of a lady who as of now has diabetes. Assuming you have type 1 diabetes, you might require more insulin. Assuming that you have type 2 diabetes, you might have to begin utilizing insulin or you might require more insulin.
When you have diabetes, your baby is at risk for some problems. These issues can occur during pregnancy and after birth. The problems happen when your glucose isn’t controlled well.
Untreated or poorly controlled gestational diabetes can hurt your baby. When you have gestational diabetes, your pancreas stays at work longer than required to produce insulin, yet the insulin doesn’t bring down your blood glucose levels. Even though insulin doesn’t cross the placenta, glucose and different nutrients do. So additional blood glucose goes through the placenta, giving the baby high blood glucose levels. This causes the baby’s pancreas to make additional insulin to dispose of the blood glucose. Since the baby is getting more energy than it requires to develop and develop, the additional energy is stored as fat.
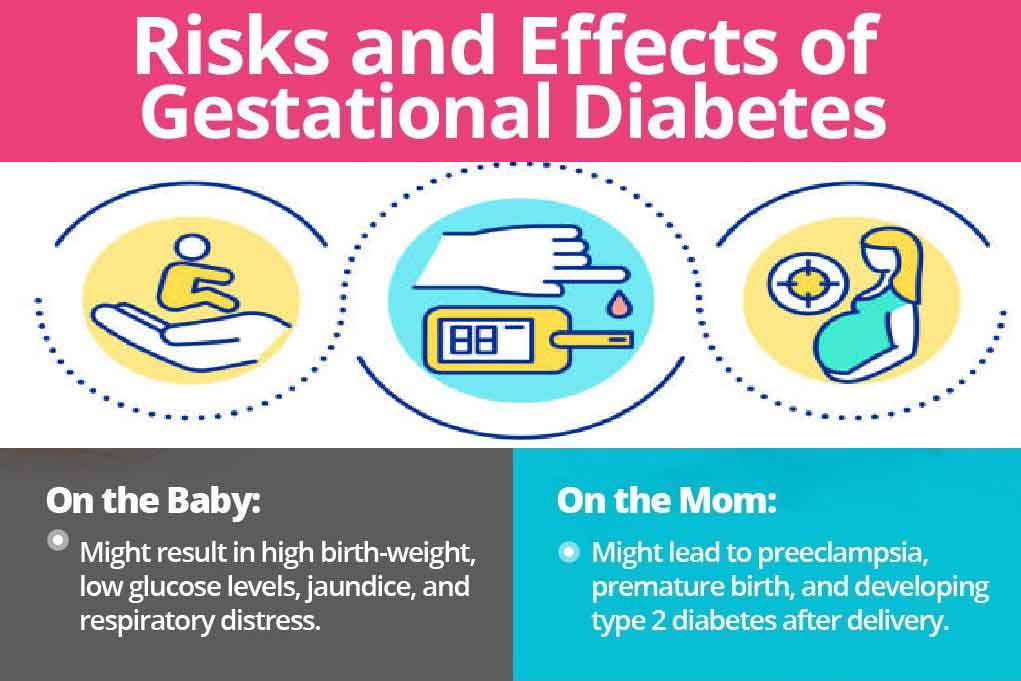
This might lead to macrosomia or a “fat” baby. Infants with macrosomia face health problems of their own, including harm to their shoulders during birth. Given the additional insulin made by the baby’s pancreas, infants might have exceptionally low blood glucose levels upon entering the world and are likewise at higher risk for breathing problems. Infants brought into the world with excess insulin become children who are at risk for obesity and adults who are at risk for type 2 diabetes.

How Will It Affect Your Baby?
Your higher glucose affects your baby, as well, since it gets nutrients from your blood. Your baby stores that additional sugar as fat, which can cause them to become larger than normal. They’re more prone to have specific complications :
- Wounds during conveyance in light of their size.
- Low glucose and mineral levels when they’re born.
- Jaundice, a treatable condition that makes the skin yellowish.
- Pre-term birth.
- Impermanent breathing problems.
As your baby grows, it could have a more prominent possibility of obesity and diabetes. So assist your youngster with carrying on with a healthy lifestyle – it can bring down their chances for these problems.
How Will It Affect You?
You might have :
- A higher chance of a C-section.
- Miscarriage.
- High blood pressure or preeclampsia.
- Pre-term birth.
Your glucose will presumably get back to business as usual after you conceive offspring. Be that as it may, you’ll have a higher risk of developing kind 2 diabetes later or gestational diabetes again with another pregnancy. A healthy lifestyle can bring down the chances of that incident. Similarly, as you can assist your kid, you with canning bring down your possibilities of obesity and diabetes.
What Symptoms Your Baby May Experience?
During pregnancy, the accompanying can happen to your baby :
- Birth defects (congenital) and premature delivery.
- High blood sugar.
- Low blood iron levels.
- Low oxygen levels.
- High blood pressure.
- Enlarged heart.
- Poor nervous system development.
- Poor lung development.
- Stillbirth.
The problems that might happen to your baby after they are born :
- Large size (macrosomia). Big infants are more liable to get injured during delivery.
- Low blood sugar (hypoglycemia).
- Low blood calcium.
- Low blood iron.
- High levels of red blood cells and thickened blood.
- High levels of bilirubin from the breakdown of red blood cells.
- Birth defects. Most affect the heart, blood vessels, brain, and spinal cord.
- Premature birth.
- Enlarged heart.
- Breathing problems.
Long haul problems. Children brought into the world to moms with diabetes are more liable to have diabetes and be obese further down the road.

Outlook
Pregnant women are sometimes tested for gestational diabetes between 24 and 28 weeks of pregnancy. Mostly, it can be controlled and treated during pregnancy. If not treated on time, gestational diabetes might cause problems for you and your baby. Usually, diabetes would disappear after your baby’s birth. But, if you’ve had gestational diabetes, you have a higher risk of being determined to have diabetes later in life.
Your baby and you require utmost care during pregnancy. Gestational diabetes and its harmful effects can be controlled. Visit Texas Speciality Care Clinic for more information.
Call us at (469) 545-9983 to book a telehealth appointment for a home check-up.

