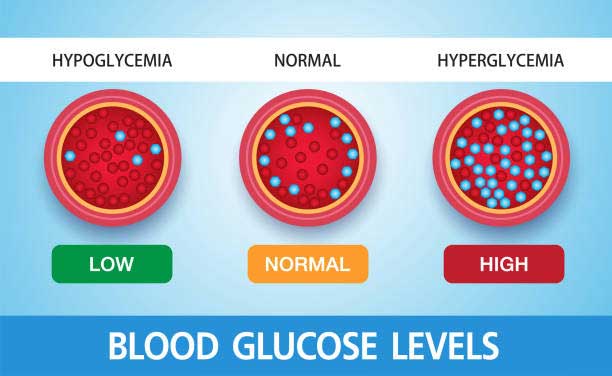
Blood glucose is a significant number with regards to diabetes the executives. High or low levels of glucose in the blood can be a sign of a serious ailment. High blood glucose levels (hyperglycemia) might be a sign of diabetes, a disorder that can cause serious, long-haul medical issues.
Low blood glucose levels (hypoglycemia) are normal among people with type 1 diabetes and people with type 2 diabetes who take specific diabetes meds. Your medical services supplier will tell you how frequently to check your blood sugar levels. The frequency of blood sugar testing relies upon the kind of diabetes you have and your treatment plan.
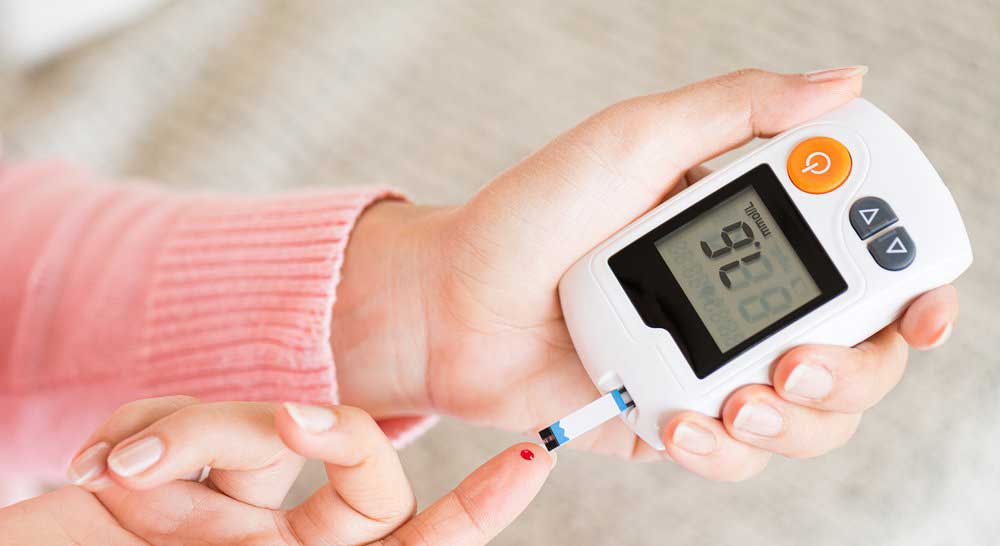
When should you get Tested for Diabetes?
Your primary care physician (PCP) might order a blood glucose test when you experience symptoms of high glucose levels or low glucose levels. Testing is necessary if you have symptoms of high blood glucose levels such as :-
- Increased thirst and urination (peeing)
- Blurred vision
- Sores that don’t heal
- Fatigue
- Unexpected Weight loss
- Numbness or tingling in your feet or hands
Or Symptoms of low blood glucose levels such as :-
- Feeling shaky or jittery
- Hunger
- Feeling dizzy, confused, or irritable
- Fatigue
- Headache
- Arrhythmia or fast heartbeat
- Difficulty seeing or speaking clearly
- Fainting or seizures
Type 1 diabetes :- Your PCP may advise blood sugar testing around 4 to 10 times a day when you have type 1 diabetes.
Type 2 diabetes :- If you take insulin to manage type 2 diabetes, your healthcare provider may recommend blood sugar testing several times a day, depending on the type and amount of insulin you use. Testing is usually recommended before meals and at bedtime if you’re taking multiple daily injections. You may need to test only before breakfast and sometimes before dinner or at bedtime if you use just an intermediate- or long-acting insulin.
Self-monitoring of blood glucose (SMBG) and Assisted Monitoring of Blood Glucose (AMBG)
With self-monitoring of blood glucose, people play out all means of monitoring for themselves. With helped monitoring of blood glucose, similar advances are followed however testing is performed for an individual or multiple people by another person (e.g., a caregiver or healthcare professional).
Assisted monitoring of blood glucose is ordinarily acted in healthcare settings like clinics, medical clinics, or hospitals, and long-term care settings (such as skilled nursing offices and assisted living amenities).
People who perform blood glucose monitoring either for themselves or others should know about essential safe practices to protect against infection transmission. These incorporate the following infection control requirements :
- Fingerstick devices, or lancing devices :- They shall never be shared, even with close loved ones. This direction incorporates both the lancet (i.e., the sharp instrument that punctures the skin) and the pen-like gadget that houses the lancet. Neither ought to be utilized for more than one person.
- Blood glucose meters :- These should not be shared. Assuming that they should be shared, the gadget should be cleaned and disinfected after each utilization (according to the manufacturer’s instructions). If the manufacturer doesn’t determine how the gadget ought to be cleaned and disinfected then it ought not to be shared.
What are the Different Types of Diabetes Tests?
Your primary care physician will have you take at least one of the following blood tests to affirm the diagnosis :-
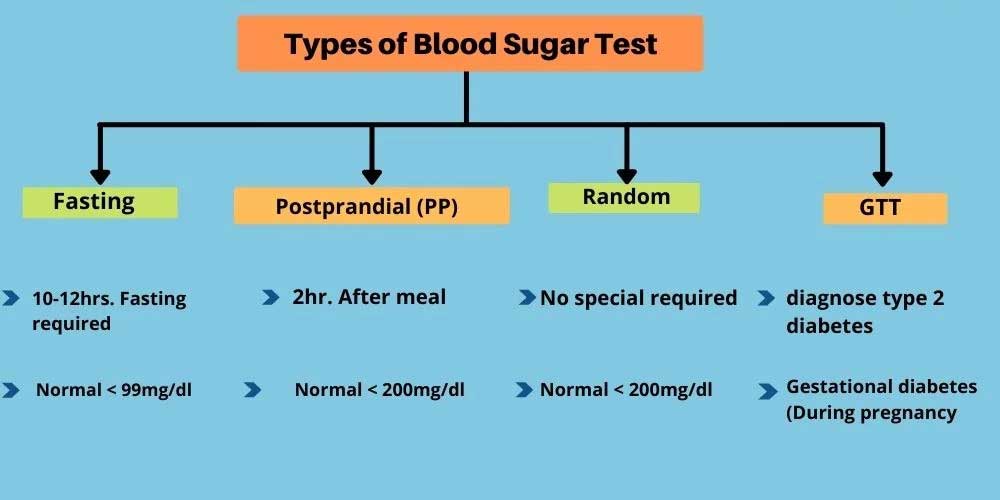
- A1C Test :- The A1C test estimates your typical blood sugar level over the beyond 2 or 90 days. An A1C below 5.7% is typical, somewhere in the range of 5.7 and 6.4% shows you have prediabetes, and 6.5% or higher demonstrates you have diabetes.
- Fasting Blood Sugar Test :- This test measures your blood sugar after overnight fasting. A fasting blood sugar level of 99 mg/dL or lower is typical, 100 to 125 mg/dL shows you have prediabetes, and 126 mg/dL or higher demonstrates you have diabetes.
- Glucose Tolerance Test :- This test measures your blood sugar when you drink a fluid that contains glucose. You’ll quick (not eat) short-term before the test and have your blood drawn to determine you are fasting blood sugar level. Then, at that point, you’ll drink the fluid and have your blood sugar level look at 60 minutes, 2 hours, and potentially 3 hours subsequently. At 2 hours, a blood sugar level of 140 mg/dL or lower is viewed as typical, 140 to 199 mg/dL demonstrates you have prediabetes, and 200 mg/dL or higher shows you have diabetes.
- Random Blood Sugar Test :- This measures your blood sugar at the time you’re tested. You can take this test whenever and don’t have to quick (not eat) first. A blood sugar level of 200 mg/dL or higher indicates you have diabetes.
- Urine Ketone Testing :- An alternate type of home test assesses the urine for the presence of ketones, which the body produces by separating fats for energy. Ketones typically show that the body has too little insulin. Most pharmacies sell these packs. The test includes gathering a urine sample, then, at that point, embedding the given strips into the urine. These will demonstrate the presence of ketones.
If your primary care physician thinks you have type 1 diabetes, your blood may likewise be tested for autoantibodies (substances that show your body is going after itself) that are many times present in type 1 diabetes but not in type 2 diabetes. You might have your urine tested for ketones (created when your body consumes fat for energy), which likewise demonstrates type 1 diabetes rather than type 2 diabetes.
Should you get Tested for Diabetes during the Gestational Period?
Gestational diabetes is diagnosed utilizing blood tests. You’ll likely be tested somewhere in the range of 24 and 28 weeks of pregnancy. If your risk is higher for getting gestational diabetes (because of having more risk factors), your PCP might test you earlier. Blood sugar that is higher than typical right off the bat in your pregnancy might demonstrate you have type 1 or type 2 diabetes as opposed to gestational diabetes.
- Glucose Screening Test :- This measures your blood sugar at the time you’re tested. You’ll drink a fluid that contains glucose, and afterward, 1 hour after the fact your blood will be drawn to check your blood sugar level. A typical outcome is 140 mg/dL or lower. If your level is higher than 140 mg/dL, you’ll have to take a glucose resilience test.
- Glucose Tolerance Test :- This measures your blood sugar when you drink a fluid that contains glucose. You’ll quickly (not eat) overnight before the test and have your blood drawn to determine you are fasting blood sugar level. Then you’ll drink the fluid and have your blood sugar level look at 60 minutes, 2 hours, and potentially 3 hours a short time later. Results can differ contingent on the size of the glucose drink and how frequently your blood sugar is tested. Ask your PCP what your test results mean.
Outlook
A blood glucose test is a significant test frequently used to analyze diabetes or to assist people with diabetes deal with their condition. Your primary care physician might arrange a blood glucose test as a component of a yearly wellness checkup. However, if you’re encountering any new symptoms of diabetes, such as expanded thirst, continuous urination, or blurred vision, talk with your PCP about blood glucose testing.
Our expert doctors help diagnose and treat your diabetes condition. Texas Speciality Care has cutting-edge medical care to diagnose any serious and chronic medical problems. Call us at (469) 545-9983 to book a telehealth appointment for a home check-up.
