Inflammation is your body’s attempt to cure itself by fighting against things that hurt it, such as infections, injuries, and toxins. When your cells are damaged, your body releases substances that cause your immune system to respond.
Chronic inflammation occurs when this response persists, keeping your body on high alert. Chronic inflammation can have a harmful influence on your tissues and organs over time. According to some studies, chronic inflammation may play a role in a variety of illnesses ranging from cancer to stroke.

What are the manifestations of chronic inflammation?
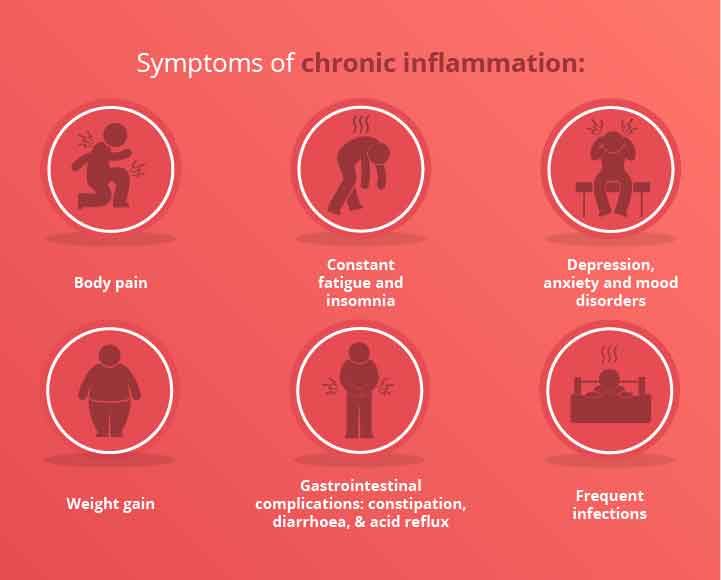
Acute inflammation frequently creates visible signs such as pain, redness, or swelling. However, the symptoms of chronic inflammation are usually considerably more subtle. As a result, they are often overlooked. Chronic inflammation is characterized by the following symptoms :
- Fatigue
- Body ache
- Anxiety or depression
- Gastrointestinal problems (diarrhea or constipation)
- Weight gain and loss
- Infections that persist
- Fever
- Mouth Sores
- Rashes
- Abdominal Pain
- Chest Pain
These symptoms can be moderate to severe and can continue for months or years.
The body can sometimes wrongly view its cells or tissues as dangerous. This reaction can result in autoimmune disorders like type 1 diabetes. When the body identifies an intruder, it initiates a biological response in an attempt to eliminate it. A foreign body, such as a thorn, irritation, or virus, could be the aggressor. Bacteria, viruses, and other creatures that cause illnesses are examples of pathogens.
Chronic inflammation is associated with or may be associated with a variety of disorders, including :-
- Diabetes and cardiovascular disease (CVD)
- Arthritis and other joint conditions
- Allergies
- COPD (chronic obstructive pulmonary disease)
- Rheumatoid arthritis and psoriasis
Inflammation measurement
When there is inflammation in the body, there are greater amounts of chemicals known as biomarkers. C-reactive protein is an example of a biomarker (CRP). CRP levels can be measured by a PCP to test for inflammation.
CRP levels are higher among the elderly and those suffering from diseases such as cancer and obesity. Diet and exercise may also have an impact.
What factors contribute to chronic inflammation?
Chronic inflammation can be caused by a variety of factors, including untreated causes of acute inflammation, such as an infection or injury; an autoimmune disorder, in which your immune system mistakenly attacks healthy tissue; and long-term exposure to irritants, such as industrial chemicals or polluted air.
Keep in mind that not everyone experiences chronic inflammation as a result of these conditions. Furthermore, certain cases of persistent inflammation lack a definite underlying cause. A variety of other variables, including smoking, obesity, alcohol, and chronic stress, may also contribute to chronic inflammation.

What is the treatment for chronic inflammation?
Inflammation is an unavoidable component of the healing process. However, if it becomes chronic, it is critical to try to regulate it to lower your chance of long-term damage. Some of the options for inflammation management that have been investigated include :
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory medications (NSAIDs) :- Aspirin, ibuprofen (Advil), and naproxen (Aleve) are examples of over-the-counter NSAIDs that efficiently relieve inflammation and pain. Long-term use, on the other hand, has been associated with an elevated risk of various illnesses, including peptic ulcer disease and kidney disease.
- Steroids :- Corticosteroids are steroid hormones. They reduce inflammation and suppress the immune system, which is beneficial when it begins to assault healthy tissue. However, long-term corticosteroid use can cause eyesight issues, high blood pressure, and osteoporosis. When your doctor prescribes corticosteroids, he or she will discuss the benefits and dangers with you.
- Supplements :- Certain nutrients may aid in the reduction of inflammation. Fish oil, lipoic acid, and curcumin have all been associated with lower inflammation – however, more research, particularly on fish oil, is needed to be certain. Several spices, including ginger, garlic, and cayenne pepper, may also aid with chronic inflammation and inflammatory disease, although further research on appropriate dosage and conclusive conclusions is needed.
- Lifestyle changes :- Weight loss (if recommended by your doctor), increased physical activity, and dietary adjustments (such as a low glycemic diet and reduced saturated fat intake) have all been demonstrated to help reduce inflammation.
What effect does nutrition have on chronic inflammation?
What you consume can have an impact on chronic inflammation in both positive and negative ways.
Foods to Eat
A wide range of foods has anti-inflammatory qualities. These include foods strong in antioxidants and polyphenols, such as
- Olive oil.
- Tomatoes with leafy greens such as kale and spinach.
- Fatty fish, such as salmon, sardines, and mackerel.
- Nuts.
- Fruits, particularly cherries, blueberries, and oranges.
Food to Avoid
Some people’s inflammation has been reported to be increased by the following foods :
- White bread and pastries are examples of refined carbs.
- fried foods, such as French fries.
- Hot dogs and sausage are examples of processed meat.
If you’re seeking to reduce chronic inflammation, your primary care physician may advise you to limit your consumption of these foods. You don’t have to fully avoid them, but try to eat them only on rare occasions.
Outlook
Chronic inflammation raises your risk of developing several dangerous diseases. Blood tests can be used by your doctor to diagnose inflammation. You can minimize your risk of inflammation by taking medication, taking supplements, and eating an anti-inflammatory diet. Avoiding smoking and alcohol, as well as maintaining healthy body weight, can help minimize your risk, as can lowering your stress levels.
Our expert primary and urgent care doctors help diagnose and treat your chronic inflammation quickly. Texas Speciality Care has cutting-edge medical care to diagnose any serious and chronic medical problems. Call us at (469) 545-9983 to book a telehealth appointment for a home check-up.

