Ultrasound Imaging: A Window into the Body
Ultrasound imaging is a valuable diagnostic tool that uses high-frequency sound waves to create images of internal organs and tissues. This non-invasive technique provides real-time images of the body’s structures, helping healthcare providers diagnose and monitor a variety of medical conditions.
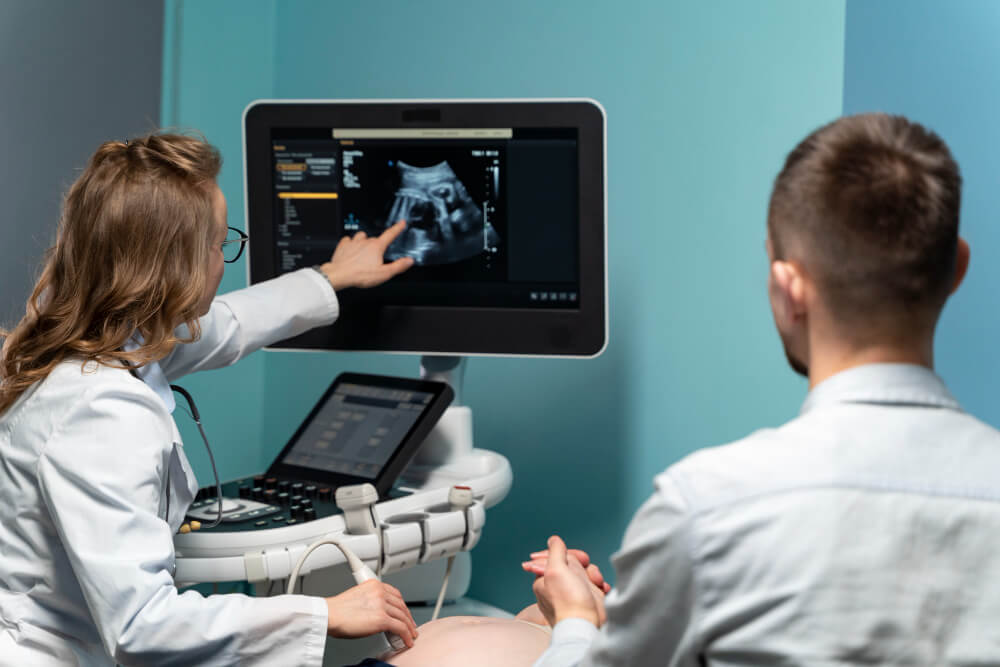
How Ultrasound Imaging Works
Ultrasound imaging works by transmitting high-frequency sound waves into the body. These sound waves bounce off tissues and organs, producing echoes that are detected by a transducer. The echoes are then converted into images that can be viewed on a monitor.
Types of Ultrasound Imaging
There are several types of ultrasound imaging, including:
- 2D Ultrasound: This is the most common type of ultrasound, providing a two-dimensional image of the structure being examined.
- 3D Ultrasound: This technique creates a three-dimensional image, providing a more detailed view of the structure.
- 4D Ultrasound: This technique adds a time dimension to 3D ultrasound, allowing for real-time visualization of movement and function.
- Doppler Ultrasound: This technique measures blood flow through blood vessels.
Medical Applications of Ultrasound Imaging
Ultrasound imaging is used in a wide range of medical applications, including:
Obstetrics and Gynecology
- Fetal Development: Ultrasound is used to monitor fetal growth and development throughout pregnancy.
- Pelvic Health: Ultrasound can help diagnose conditions such as ovarian cysts, fibroids, and endometriosis.
Cardiology
- Heart Function: Ultrasound, also known as echocardiography, is used to assess heart function, identify heart defects, and monitor the effects of heart disease.
Abdominal Imaging
- Liver, Gallbladder, and Pancreas: Ultrasound can be used to diagnose conditions such as gallstones, liver disease, and pancreatitis.
- Kidneys and Bladder: Ultrasound can help identify kidney stones, kidney cysts, and bladder abnormalities.
Vascular Imaging
- Blood Vessel Disease: Ultrasound can be used to assess blood flow in arteries and veins, helping to diagnose conditions such as atherosclerosis and deep vein thrombosis.
Musculoskeletal Imaging
- Muscle and Tendon Injuries: Ultrasound can help diagnose injuries to muscles, tendons, and ligaments.
- Joint Conditions: Ultrasound can be used to assess joint inflammation and cartilage damage.
Advantages of Ultrasound Imaging
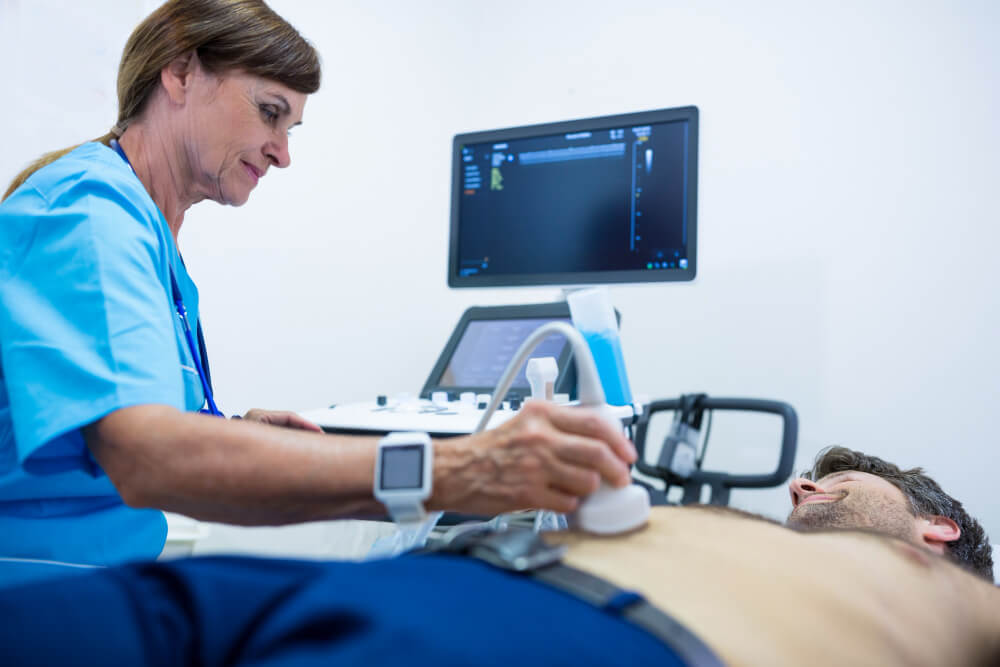
- Non-invasive: Ultrasound imaging is a non-invasive procedure that does not involve radiation exposure.
- Painless: The procedure is typically painless, making it suitable for patients of all ages, including children and the elderly.
- Real-time Imaging: Ultrasound provides real-time images, allowing healthcare providers to assess the structure and function of organs and tissues.
- Portability: Ultrasound machines are portable, making it possible to perform imaging at the bedside or in remote locations.
- Cost-Effective: Ultrasound is a relatively affordable imaging modality compared to other techniques such as CT scans and MRIs.
Preparing for an Ultrasound Exam
Before undergoing an ultrasound exam, it’s important to follow your healthcare provider’s instructions. In some cases, you may need to fast or drink plenty of fluids beforehand. During the exam, you may be asked to change into a gown and lie down on an exam table. The technician will apply a gel to the skin to help transmit the sound waves.
Conclusion
Ultrasound imaging is a valuable diagnostic tool that offers numerous benefits. It is a safe, painless, and non-invasive procedure that can provide valuable insights into a wide range of medical conditions. By understanding the principles of ultrasound imaging and its applications, patients can make informed decisions about their healthcare.
Reach out to our clinic’s Diagnostic services for ultrasound imaging (469) 496-2456 Or visit us https://texasspecialtyclinic.com/
