Understanding and Overcoming Tennis Elbow: From Pain to Play
Tennis elbow, also known as lateral epicondylitis, is a common condition that causes pain on the outside of the elbow. While often associated with tennis players, it can affect anyone who performs repetitive activities that involve gripping or twisting the wrist. This article delves into the world of tennis elbow, exploring its causes, symptoms, and various treatment options to help you understand and overcome the pain, ultimately leading you back to your desired activities.
What is Tennis Elbow?
Tennis elbow is an overuse injury that occurs when the tendons connecting the forearm muscles to the outside of the elbow bone become inflamed and irritated. These tendons are responsible for extending your wrist and fingers. Repetitive movements that strain these tendons, such as gripping a racket or using tools, can lead to micro-tears in the tendons, causing pain and discomfort.
Causes of Tennis Elbow
While the name suggests a connection solely to tennis, various activities can contribute to tennis elbow. Here are some common causes:
- Repetitive gripping or twisting motions: This includes activities like using screwdrivers, painting, playing racket sports like badminton and squash, and even typing for extended periods.
- Improper technique: Incorrect form during activities like weightlifting, using a computer mouse, or playing sports can put increased stress on the elbow tendons.
- Weak forearm muscles: Weak muscles can make the tendons work harder, increasing the risk of injury.
- Age: As we age, our tendons become less flexible and more susceptible to overuse injuries.
Symptoms of Tennis Elbow
The most common symptom of tennis elbow is pain on the outside of the elbow, just below the bony bump. This pain can worsen with activities like gripping, lifting objects, or extending the wrist. Other symptoms may include:
- Weakness in the forearm
- Tenderness to touch
- Pain that radiates down the forearm towards the wrist
- Difficulty gripping objects
Diagnosis of Tennis Elbow
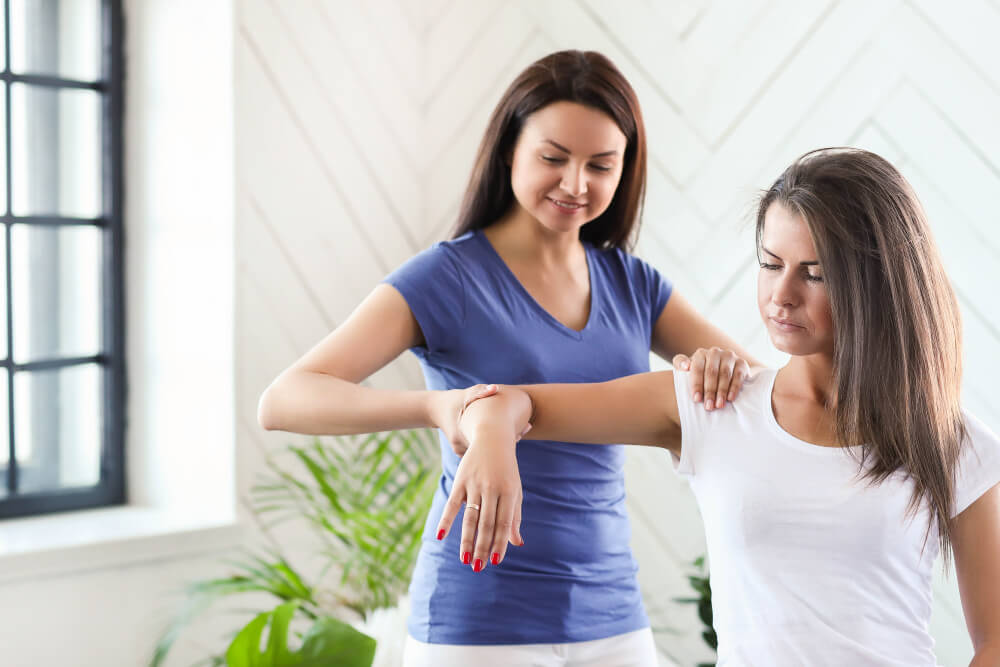
Diagnosing tennis elbow typically involves a physical examination by a doctor or physiotherapist. They will inquire about your symptoms, medical history, and any activities you perform that might be contributing to the pain. They may also perform tests to assess your range of motion, tenderness, and strength in your arm and hand. In some cases, imaging tests like X-rays or ultrasounds might be necessary to rule out other causes of elbow pain, such as fractures or arthritis.
Treatment Options for Tennis Elbow

The good news is that most cases of tennis elbow respond well to conservative, non-surgical treatment. Here are some common treatment options:
Rest and Activity Modification:
The most important step towards recovery is rest. This involves avoiding activities that aggravate the pain, allowing the inflamed tendons time to heal. Modifying your activities to minimize strain on the elbow can also be crucial.
Ice Therapy:
Applying ice packs to the affected area for 15-20 minutes, several times a day, can help reduce inflammation and pain.
Compression:
Wearing a compression brace around the forearm can provide support and reduce swelling.
Pain Medication:
Over-the-counter pain relievers like ibuprofen or acetaminophen can help manage pain and inflammation.
Physical Therapy:
A physiotherapist can design a personalized exercise program to strengthen the forearm muscles, improve flexibility, and correct any imbalances that might be contributing to the problem. Stretches and strengthening exercises are crucial for long-term recovery and preventing future flare-ups.
Corticosteroid Injections:
In cases where other treatments fail to provide relief, a doctor might inject a corticosteroid medication directly into the inflamed area to reduce inflammation. However, this is usually a last resort due to potential side effects with repeated injections.
Extracorporeal Shock Wave Therapy (ESWT):
This non-invasive therapy uses sound waves to stimulate tissue healing and promote blood flow to the affected area. However, the effectiveness of ESWT for tennis elbow is still under investigation.
Surgery:
In rare cases where conservative treatments fail to provide long-term relief, surgery might be an option. The specific type of surgery depends on the severity of the injury and the location of the tear.
Preventing Tennis Elbow
Preventing tennis elbow is always better than treating it. Here are some tips:
- Warm up and cool down: Perform gentle stretches and light activity before and after engaging in strenuous activities.
- Maintain proper form: Ensure proper technique during sports, weightlifting, or any activity that involves your arms and wrists.
- Strengthen your forearms: Regularly perform exercises to strengthen the muscles in your forearm, which can help support the tendons and reduce stress.
